How do Vaccines Work? Enjoy our new manuscript for young minds.
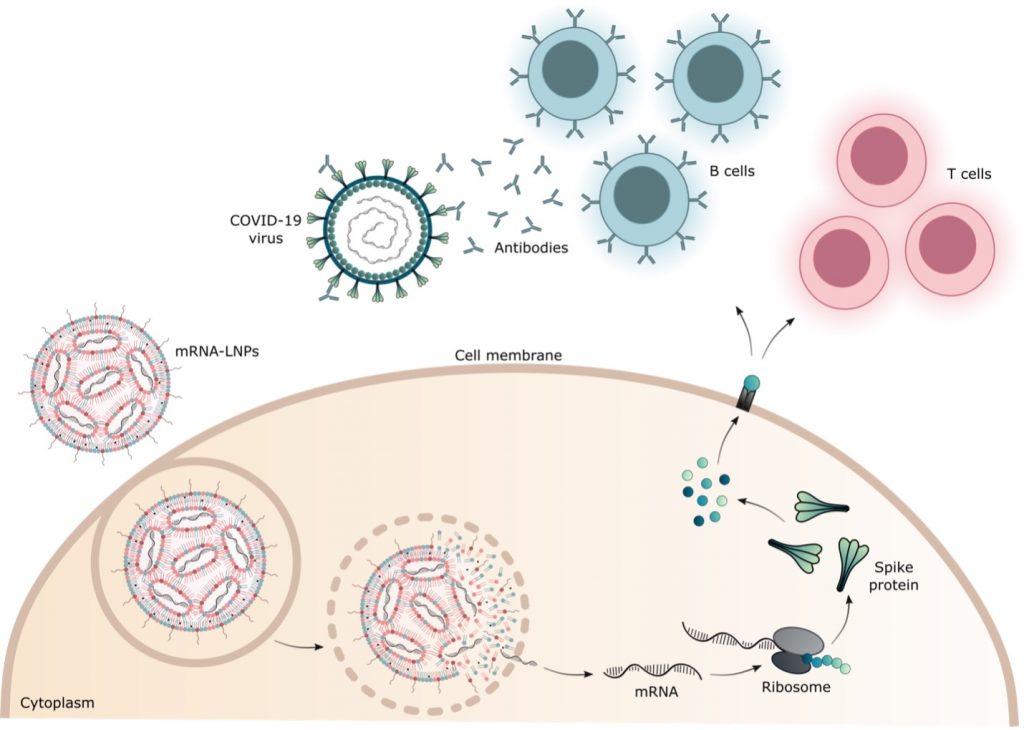
mRNA-LNP vaccines are injected into the muscle, where they are swallowed by muscle and immune cells. After entering the cells, the mRNA-LNPs release their mRNA molecules into the cell’s cytoplasm.
In the cytoplasm, ribosomes “read” the code on the mRNA, using it to create the viral spike protein. When the spike protein breaks down inside cells, small pieces are moved to the cell membrane, where they are “shown” to T and B cells.
These immune cells recognize the spike protein as foreign (not from a human) and create an immune response, including antibodies against it. Eventually, the mRNA from the vaccine breaks down and all that remains is the immune system’s memory.
Hazan-Halevy I, Kon E, Stotsky-Oterin L, Peer D. Frontiers for Young Minds 2023. Full article
